There are AI-powered academic search engines that uses generative AI from large-language models (LLM) to generate contextually appropriate responses to prompts using retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) techniques. RAG technique aims to address AI hallucination by training LLMs to make use of trusted documents such as existing peer-reviewed articles and academic papers to draw information from.
"RAG provides a way to optimize the output of an LLM with targeted information without modifying the underlying model itself; that targeted information can be more up-to-date than the LLM as well as specific to a particular organization and industry. That means the generative AI system can provide more contextually appropriate answers to prompts as well as base those answers on extremely current data" (Zeichick, 2023, para. 3). In simple terms, "RAG helps LLMs give better answers." (Zeichick, 2023, para. 7)
RAG includes two primary actors: the retriever (i.e. sleuth) and the generator (i.e. storyteller) (Ghodgaonkar & Staten, 2023).
The Retriever (the “Sleuth”): This is the model that retrieves relevant documents. Usually, these documents (pdf files, text/csv files, web scrapes, etc.) are stored as embeddings in a vector database, and the retrieval capability is built directly into the vector database.
The Text Generator (the “Storyteller”): The LLM that generates text output.
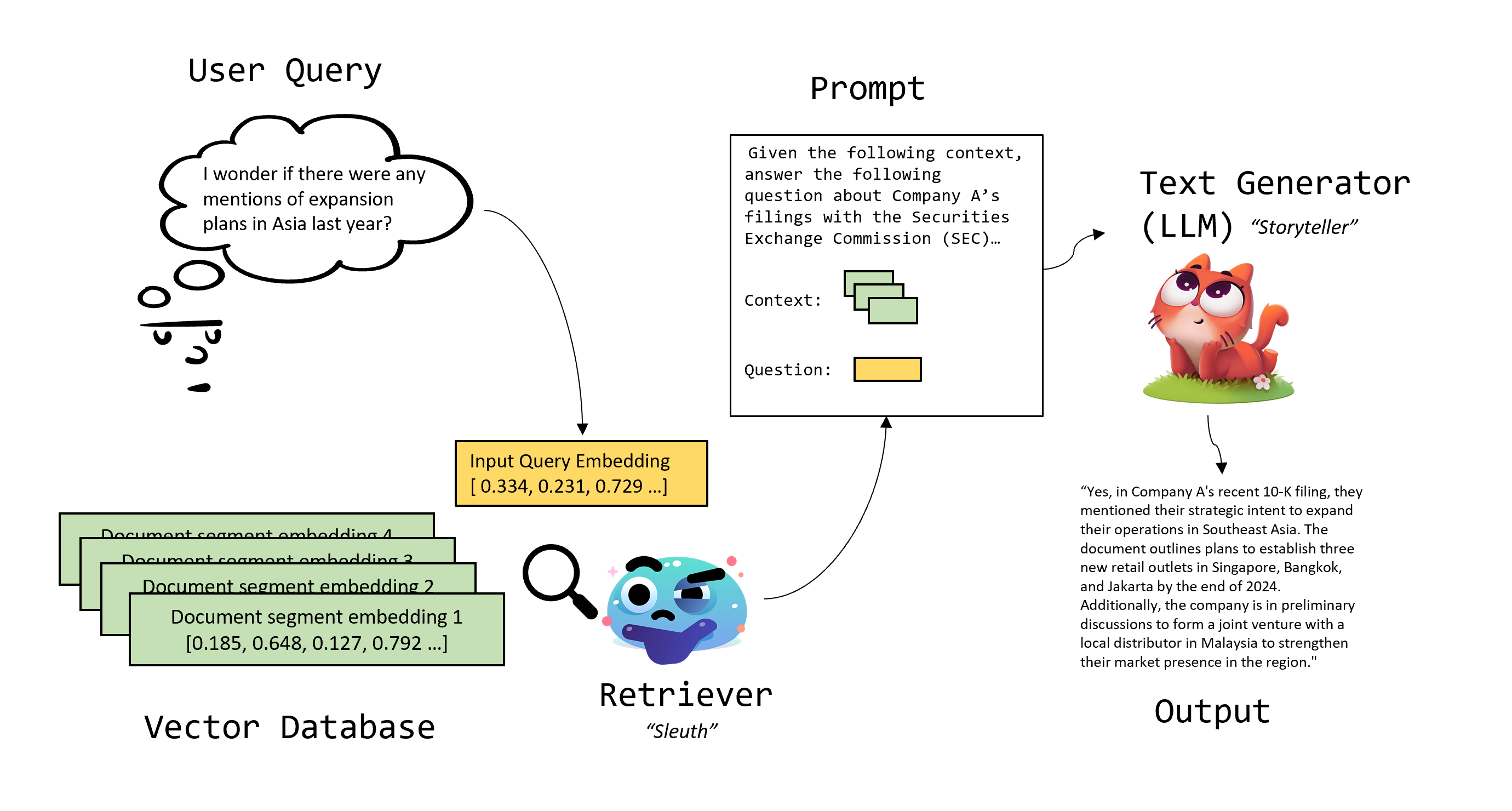
Image credit: Ghodgaonkar, I. & Staten, C. (2023). The Sleuth and the Storyteller: The Dynamic Duo behind RAG. DeterminedAI. https://www.determined.ai/blog/rag
Source: Zeichick, A. (2023, Sept. 19). What is retrieval-augmented generation (RAG)?. OCI. https://www.oracle.com/artificial-intelligence/generative-ai/retrieval-augmented-generation-rag/
Aside from RAG which allows generative AI to ingest information from reliable sources of information to create contextually relevant, timely, and more accurate responses, as responsible scholars, we can also use the conventional and trusted ways of searching such as keyword and semantic search.
Keyword search allows you to break down your research questions, statement, or topics into concepts. These are words that best describe your topics which include various terminologies such as jargon terms, related terms, or even subject terms that you can use to retrieve relevant information on your topic which usually found in book and article titles.
On the other hand, Semantic search, it is a step beyond keyword searching wherein the context and understanding is more prioritized even when the words or titles seems to not make sense. It is a bit like a librarian, who understands what your searching and provides similar and relevant information even beyond the keywords.
Gu, J. (2024, Mar. 20). Five AI research tools that referencing genuine sources reviews. Research Bridge. https://library.hkust.edu.hk/sc/ai-tools-with-genuine-sources/
Tay, A. (2024, Aug.). List of academic search engines that use large language models for generative answers (updated to Aug 2024). Aaron Tay's Musings about Librarianship. https://musingsaboutlibrarianship.blogspot.com/p/list-of-academic-search-engines-that.html
Zeichick, A. (2023, Sept. 19). What is retrieval-augmented generation (RAG)?. OCI. https://www.oracle.com/artificial-intelligence/generative-ai/retrieval-augmented-generation-rag/
Zhao, A. (2024, Mar. 20). Trust in AI: Evaluating Scite, Elicit, Consensus, and Scopus AI for generating literature reviews. Research Bridge. https://library.hkust.edu.hk/sc/trust-ai-lit-rev/